How to Successfully Roll Out an AI Chatbot for Internal Employees
Ready to launch your chatbot? We've helped businesses roll out more than 150 AI agents and chatbots for internal employees, trusted by Fortune 500 companies worldwide. In short, we know exactly what it takes to turn a chatbot idea into a success story.

Studies show that over 70% of employees are afraid to ask questions at work, fearing judgment or rejection. This silence can quietly stifle innovation and slow organizational growth.
At the same time, employees spend about 30% of their workday searching for information — often across a fragmented ecosystem of apps and tools (the average company now uses around 130 collaboration apps). This not only wastes time but also frustrates teams and disrupts productivity. Acting as an always-available, all-knowing teammate, a chatbot for internal employees can help employees find precisely what they need — instantly.
Learn how to roll out an internal chatbot that becomes everyone's daily go-to — not just another shiny idea that dies in the drawer.
What Is a Chatbot for Internal Employees?
A chatbot for employees is an AI-powered assistant designed to help employees inside an organization. It streamlines everyday tasks such as answering FAQs, retrieving company policies, sharing documents, or even automating routine workflows — all through natural conversation.
By making information instantly accessible, internal chatbots reduce friction, save time, and improve productivity across departments like HR, IT, and Operations.
Your Step-by-Step Guide to Launching an AI Chatbot Employees Will Love
Building a chatbot for employees today is easier than ever thanks to a wide range of dedicated tools. But creating an internal chatbot that truly works for your organization is a different challenge altogether. It's not just about making it smart or personalized — it is about designing a tool that employees actually want to use.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key steps to successfully launch an internal chatbot across your company so you can ensure a smooth rollout and lasting results.
Step 1. Define the “Why” Behind the Chatbot
Before you explore tools or launch pilot projects, take a step back and clarify why your organization wants to adopt AI in the first place. A well-defined purpose will guide every decision that follows — from selecting the right technology to ensuring long-term impact.
Start with your business goals: what do you want your internal chatbot to achieve for your employees? Are you aiming to save time on repetitive tasks, reduce the workload for HR or IT teams, improve access to company information, or enhance overall employee experience?
Pinpoint your pain points: look for repetitive, time-consuming, or error-prone processes that drain resources or frustrate teams. These areas often present the best opportunities for AI to deliver measurable value.
Ensure strategic alignment: consider how AI fits within your company's broader priorities, culture, and long-term objectives. When aligned with business strategy, AI becomes a true enabler, not just another tech experiment.
If you don’t already have a documented strategy, start by listing your company's top objectives. Typical goals might include:
- Increasing efficiency and productivity
- Improving customer or employee experience
- Reducing operational costs
- Strengthening regulatory compliance
- Enhancing decision-making with better data insights.
Resolve at least 60% of employee queries automatically with AI-Powered chatbots.
Step 2: Identify Key Employee Needs & Chatbot Use Cases
Before building your internal chatbot, you need to get to know your “customers” — your employees. Think like a detective: who are they, what tasks do they struggle with, which language do they use to describe their needs, and how do they currently navigate workflows?
Use existing internal data — helpdesk tickets, knowledge base searches, survey results, or HR analytics — to spot recurring issues. These insights help you pinpoint where automation can have the biggest impact.
Map the employee journey. Just as customer journey maps trace the path from awareness to purchase, employee journey maps show how staff move from task initiation to resolution. This helps you uncover:
Pain points: Repetitive, confusing, or time-consuming tasks that frustrate employees.
Roadblocks: Situations that currently require human intervention (e.g., IT troubleshooting, HR approvals).
Common requests: Frequently asked questions or routine tasks employees need help with.
High-volume interactions: Processes or topics that generate the most inquiries and could benefit most from automation.
Once you've analyzed these patterns, gather ideas directly from employees. Ask them: "What's one task you wish a chatbot could handle for you?” You'll quickly collect a list of potential use cases — from checking leave balances or booking training sessions to reporting IT issues or finding company policies.
These tasks may seem small, but they carry high frustration potential — making them perfect candidates for automation. This step is often the easiest, yet it lays the foundation for a chatbot that employees will actually use and appreciate.
For each use case, assess the potential ROI, complexity, and risk for each use case to determine where to begin. For a detailed guide, read our article on AI Use Case Evaluation.
Step 3: Prioritize by Value, Complexity, and Impact
Once you've mapped out all the user stories for your internal chatbot, it's time to determine which ones are actually worth automating. Not every interaction needs to be handled by AI — focus on those that will deliver the most significant business value and employee impact.
For each user story, assess three factors:
#1. Criticality — How essential is this task for day-to-day operations? (If it stops working when delayed, it's critical.)
#2. Complexity — How technically feasible is it to automate? (Simple lookups are easier to automate than multi-step workflows with many dependencies.)
#3. Benefit (ROI) — How much time or cost will automation save, and how often is it used? (A high-frequency but low-effort task might bring only modest ROI, whereas automating a complex but time-draining process could deliver a major impact.)
You can create a simple 1–3 scoring system for each category, then add them up to prioritize:
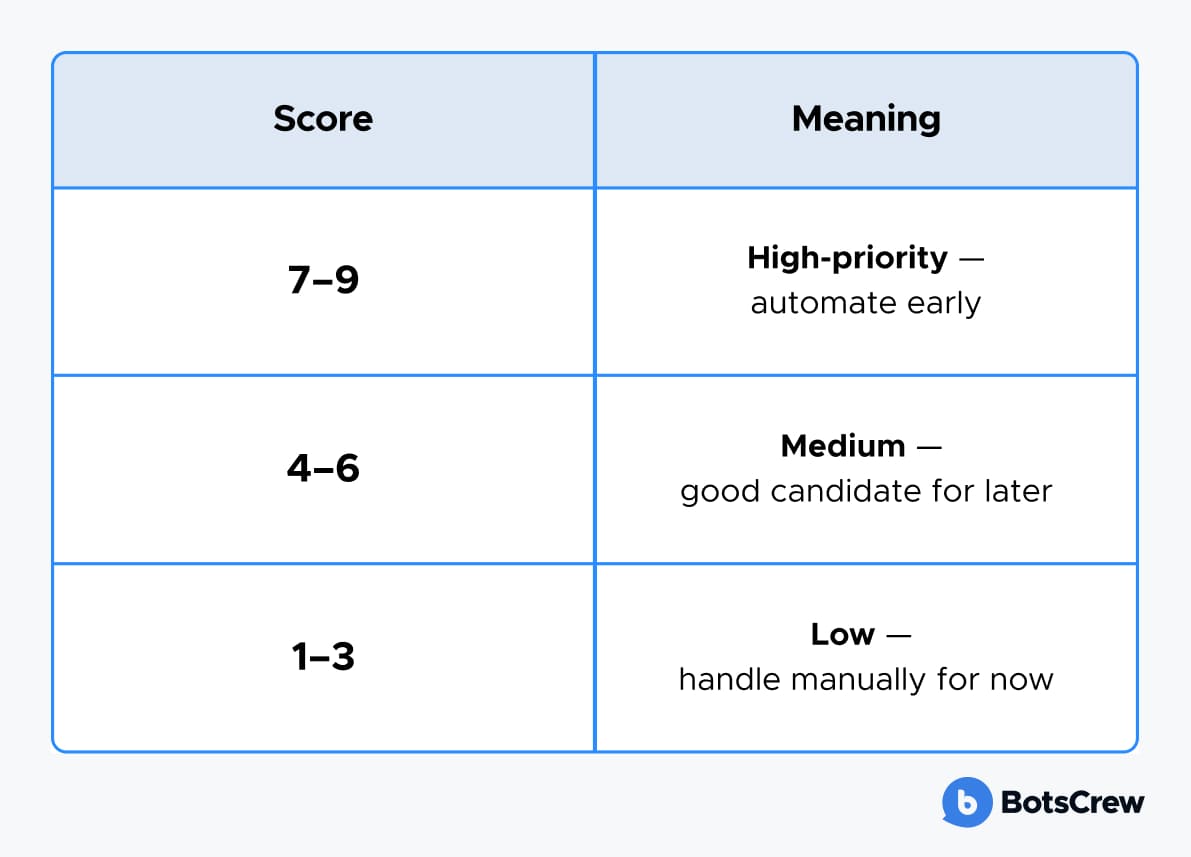
This approach ensures your internal chatbot tackles high-value, feasible use cases first, instead of just the easiest or most popular ones.
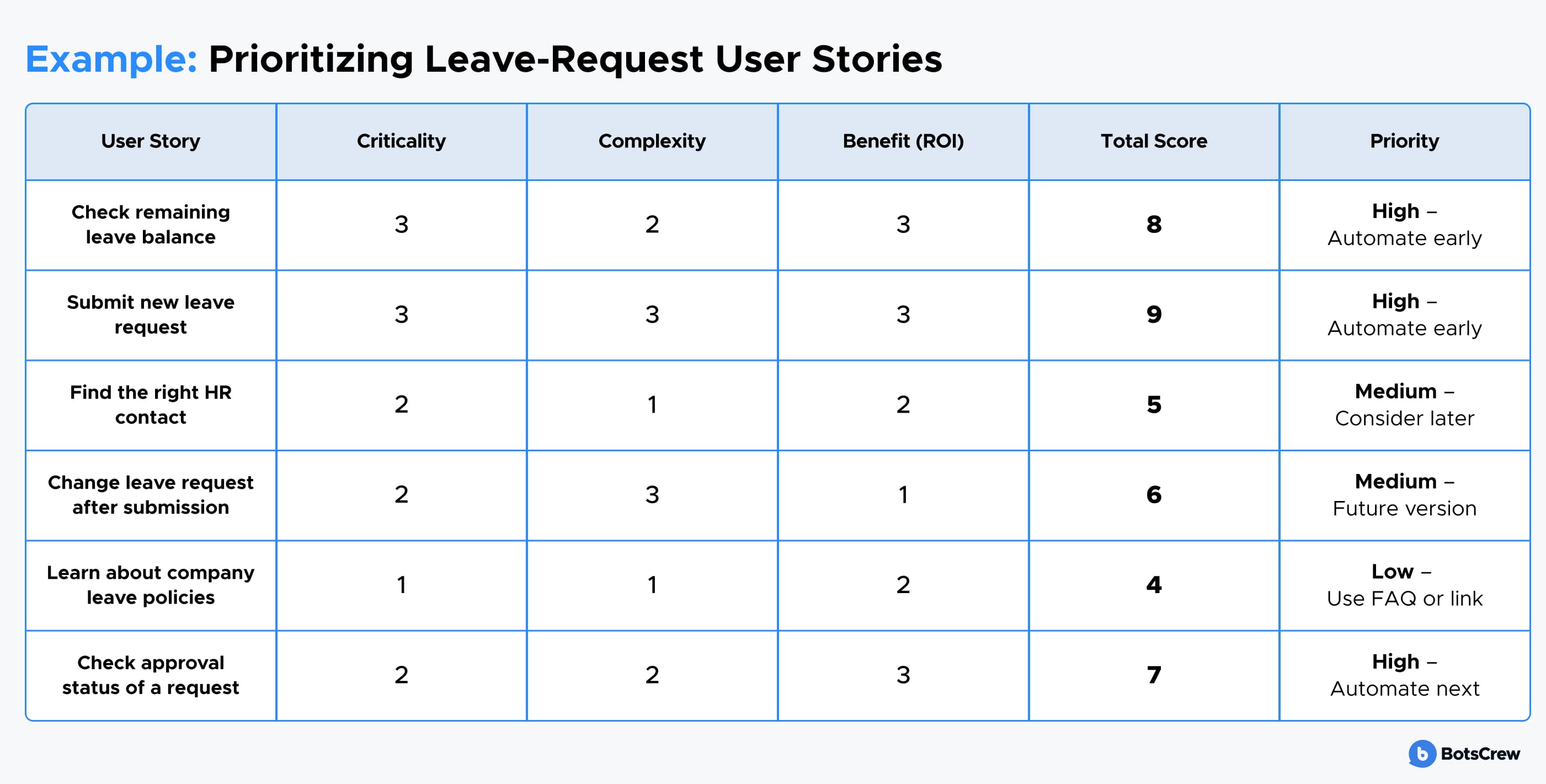
Let's take a standard internal process — requesting annual leave — and break it into user stories. Each story is scored by Criticality, Complexity, and Benefit (ROI) on a scale of 1–3.
Step 4: Map Out User Stories
Once you've identified your chatbot use cases, the next step is to break them down into user stories — the individual interactions that make up each use case.
Think of a simple example like resetting a forgotten password:

Each of these steps is a separate user story your chatbot for employees needs to handle. The goal here isn't to overcomplicate — it is to ensure your chatbot covers all the interactions employees actually need, so it feels reliable and genuinely helpful.
To make it even clearer, let's walk through a more detailed example: Leave Request User Stories.
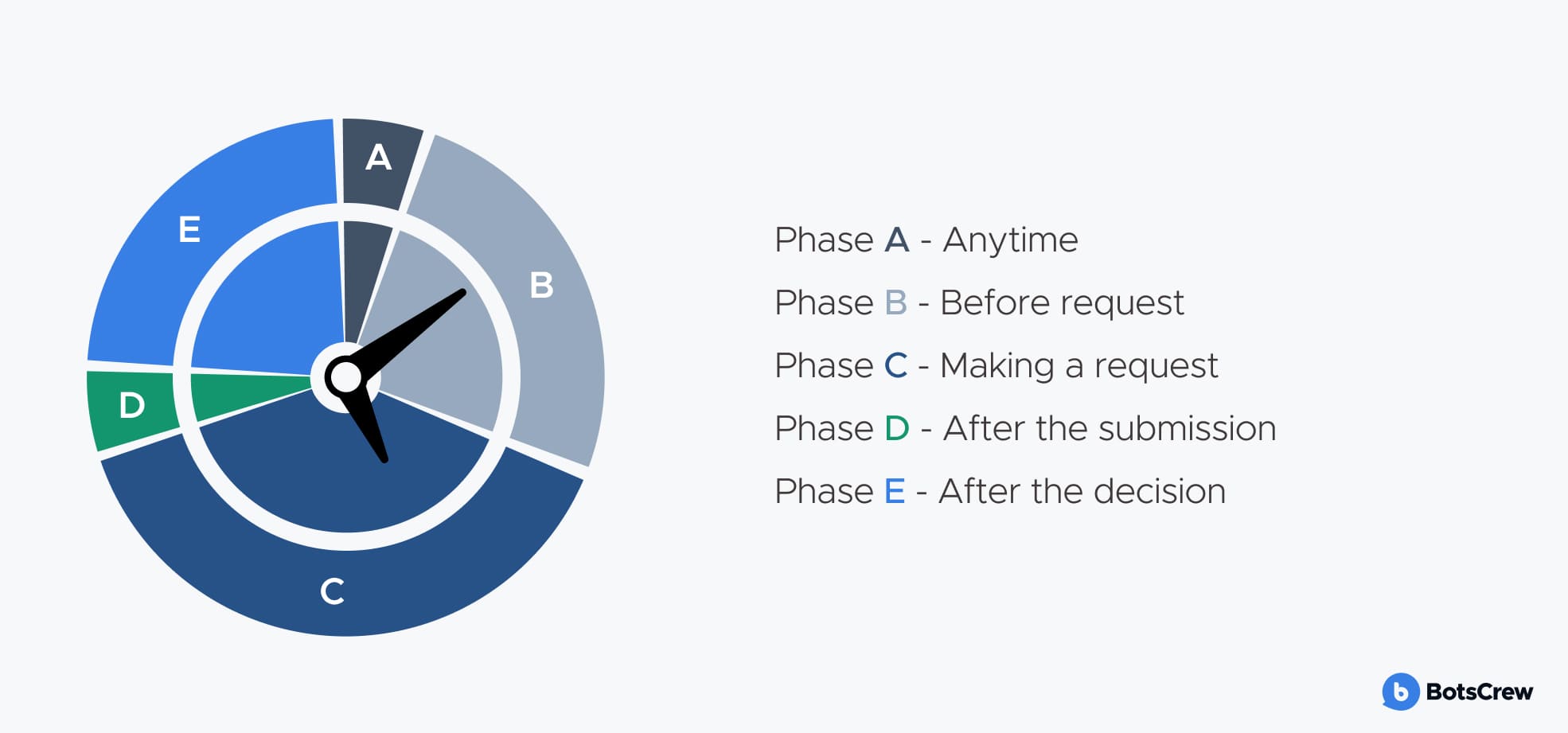
A) Anytime — Policies & Reference
- Which leave types apply? (e.g., annual leave, maternity, religious/national holidays)
- Are some policies only relevant to specific employees?
B) Before Request — Preparation
- How much leave is available? (Check HR or shift-planning software)
- Who can answer questions? (HR, supervisors, or IT, depending on the query)
C) Making a Request — Submission
- Where is the form located? (Single portal or multiple forms depending on leave type)
- Can requests be submitted via API? (Ensures chatbot for employees can automate submissions)
- If no API exists, consider system updates to enable one.
D) After Submission — Tracking
- Can requests be edited after submission?
- Can employees track the status of their request?
E) After the Decision — Outcome & Follow-Up
- How will employees be notified? (Could the chatbot deliver updates instead of email?)
- What's the procedure for informing colleagues and clients? (Out of Office messages, calendar events)
- Will work handoffs be handled efficiently?
Manager Perspective — Approvals & Oversight
- How can managers approve or decline requests via the chatbot?
- What questions might they ask, and how should the chatbot for employees respond?
Even a seemingly simple task like a leave request quickly expands into a complex lattice of user stories, variables, and conditions. A successful internal chatbot must remove friction at every stage, or employees may stop using it altogether.
Step 5: Choose the Right Platform and Build Your Chatbot
This step involves selecting the right platform and building your bot around real employee questions, workflows, and available integrations (like APIs or internal systems). Before diving in, decide how you'll develop and manage your chatbot for employees. Depending on your company's resources, timeline, and technical maturity, you'll typically choose between one of three approaches:
#1. DIY or Open-Source Solution. This route gives you maximum control and customization. You can design, prototype, build, test, deploy, and evolve the chatbot entirely in-house, often using open-source frameworks.
✅ Pros: Complete flexibility, full data ownership, tailored design for internal workflows.
⚠️ Cons: Requires significant development time, technical expertise, and ongoing maintenance.
#2. Extensible Platform. Think of this as a middle ground between a DIY build and a fully managed solution. These platforms come with hosting, built-in integrations, security support, and expert guidance — while still offering room for customization.
✅ Pros: Faster deployment, flexible configuration, easier integration across departments.
⚠️ Cons: Still requires some technical setup and understanding of internal systems.
#3. Closed Proprietary Solution. These are ready-to-use chatbot products — often designed for specific functions like HR helpdesks or IT support. They are the quickest to implement and easiest to maintain, but are typically less flexible.
✅ Pros: Rapid deployment, low maintenance, cost-effective for focused use cases.
⚠️ Cons: Limited customization, potential vendor lock-in, and reduced integration capability with existing systems.
If your goal is long-term integration across departments, an extensible platform is often the best balance between speed and adaptability.
Avoid Common Pitfalls When Launching an Internal AI Chatbot. Read our blog post: Why Internal Chatbots Fail — and How to Prevent It
Step 6: …Or Choose the Right Chatbot Partner
Not every company needs — or wants — to build its custom chatbot in-house. Maybe your team is small and strapped for time, or perhaps your AI ambitions stretch beyond your current technical capabilities. In either case, partnering with an external expert can be the smarter move.
Why work with a chatbot development partner? Partnering with an experienced provider can save your team both time and resources:
💡 No need to buy or maintain your own software
⚡ Accelerated development timelines, thanks to pre-built frameworks and proven workflows
🧠 Access to specialized expertise in AI, UX, and enterprise integrations
💰 Cost efficiency when you don’t have in-house technical skills.
💬 Check our article: 12 Questions to Ask Before Hiring an AI Development Company — a practical guide for business leaders who want real results and measurable ROI.
At BotsCrew, we've delivered bespoke AI development services for Fortune 500 companies and fast-growing startups alike. Drawing on years of experience, we help businesses move from idea to impact, developing AI agents that don't just work but deliver measurable value. And we don't stop at launch. We are focused on creating long-term success by ensuring every solution is maintainable, scalable, and built around your team’s real-world needs.
No matter who you choose, make sure your partner is familiar with your industry or use case, skilled in your chosen AI platform or architecture, and ready to provide post-launch support and optimization.
What's Next? See our AI solutions in action.
Step 7: Give Your Internal Chatbot a Personality
Many companies stop at functionality when building an internal chatbot — focusing only on what it can do, not how it communicates. But personality matters just as much for employee chatbots as it does for customer-facing ones.
Your chatbot represents your company's culture. If your workplace is open, friendly, and collaborative, your bot should sound that way too. On the other hand, a more formal organization might want a polite, concise tone that fits internal communication norms.
To define your chatbot's personality, start by asking:
- What role does the bot play in your team? (e.g., helpful assistant, IT sidekick, HR buddy)
- What's its purpose? (to guide, support, automate, inform?)
- How does it “speak” — friendly and casual, or professional and direct?
- What are its strengths and limits? (and how does it acknowledge them?)
Remember, the more your bot feels like a natural part of your company culture, the more employees will enjoy using it — and the faster they'll adopt it.
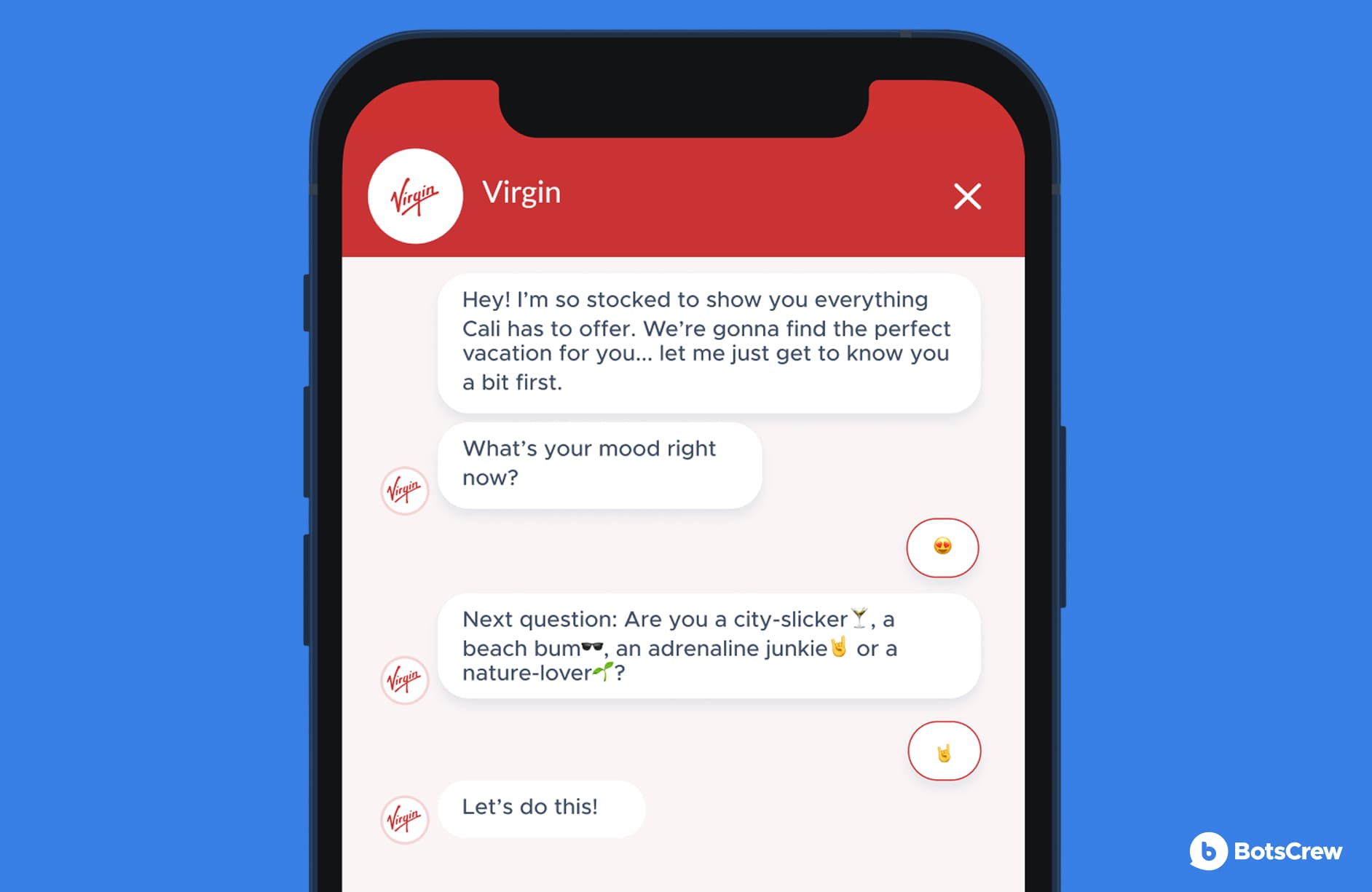
For instance, we created a chatbot for one of our clients that “speaks” with a Californian accent. Here is a glimpse of it in action.
Step 8: Design a Natural Flow of Conversation
Once your chatbot has a defined role and tone of voice, it's time to map out how it will talk to employees. Internal conversations should feel effortless and intuitive — guiding users toward answers or actions without friction.
Here's how to structure your conversation flow:
👋 Introduction:
How will your chatbot greet employees? Keep it light, friendly, and aligned with your internal culture.
“Hi there! I'm Ava from HR. Need help with time-off requests or benefits?”
💬 Information exchange:
When collecting or confirming details, prioritize clarity and speed over personality. Employees want solutions, not small talk.
“Got it — how many days of annual leave would you like to request?”
❓Handling confusion:
Even with advanced AI, misunderstandings happen. Prepare your bot to recover gracefully.
“Hmm, I'm not sure I understood that. Could you rephrase or pick from these options?”
🕓 Non-verbal communication:
If your bot needs time to fetch data from systems (like Workday or Jira), keep the employee informed to prevent frustration.
“One moment — I'm checking your leave balance.”
🎉 Fulfillment messages:
When a request is completed successfully, celebrate it in a way that feels personal but appropriate.
“Done! Your leave request has been submitted to your manager. 🌴 Have a great break!”
These subtle touches create smoother, more human-like interactions that encourage employees to keep using your chatbot as part of their everyday workflow.
Step 9: Launch Your Chatbot
After all the designing, building, and testing, it's time to roll out your AI chatbot to your employees. 🎉
Depending on your tech stack, you can deploy the bot across the communication channels your employees already use:
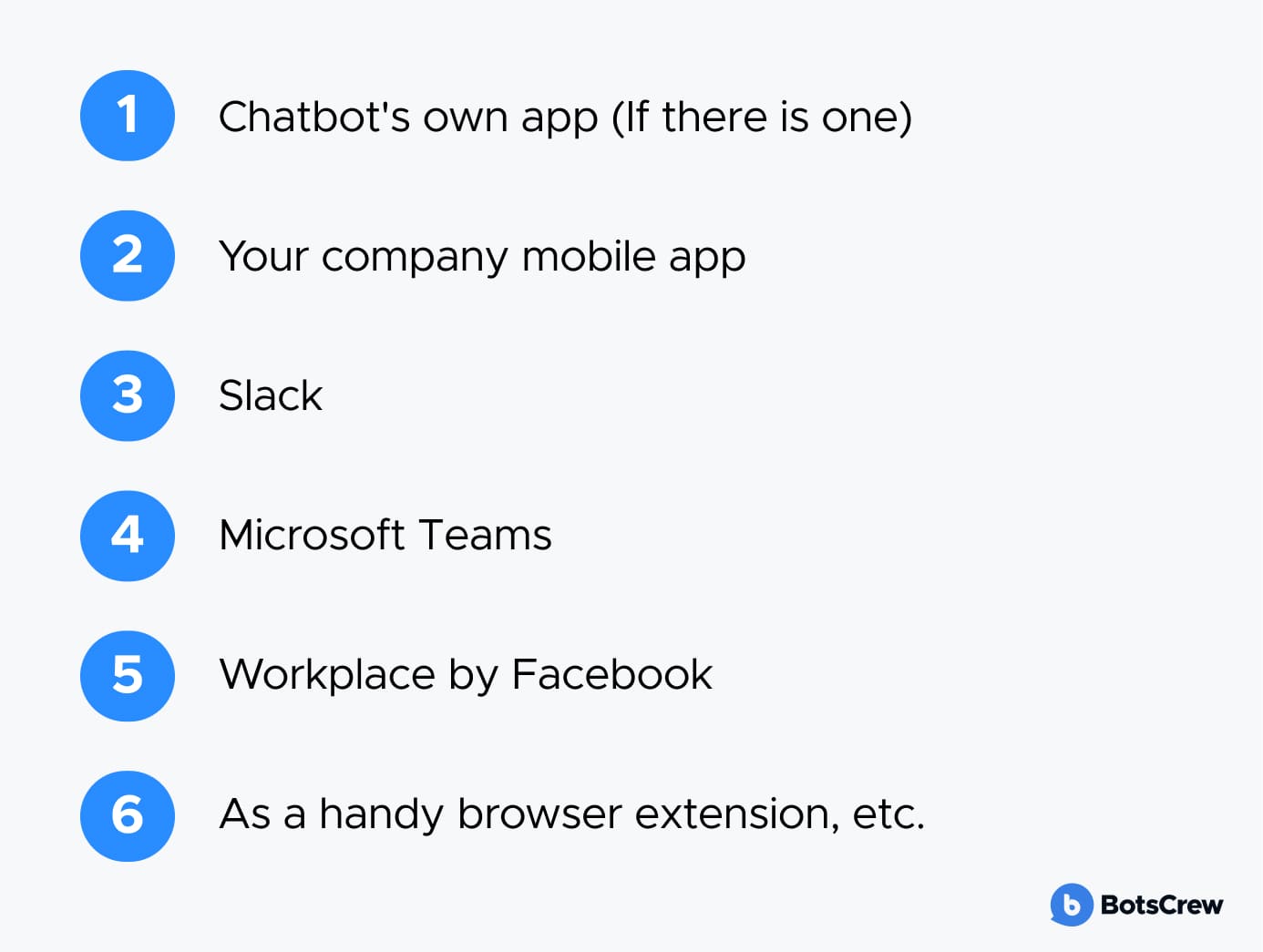
For your MVP, start small: launch on the one or two platforms where daily work already happens. This helps ensure high adoption and relevant feedback.
Before rolling out company-wide, invite a small group of employees (your “beta testers”) to try the chatbot in real scenarios. A few tips to make this phase effective:
✅ Announce the launch in the same channel where the bot lives — for example, post an introduction message in Slack or Teams.
✅ Set up a quick survey or feedback form so testers can share their thoughts easily.
✅ Encourage ideas — let employees vote on the following features they'd like to see.
✅ Give your bot a name! A friendly, memorable name makes the chatbot feel more approachable.
✅ Add a visual reminder — like a small banner or intranet card — that introduces the chatbot and its use cases.
Step 10: Monitor Engagement and Performance
Once your internal chatbot is live, the real work begins — continuous optimization. The goal is to keep it running and ensure it delivers measurable impact and evolves with your employees' needs.
Forget traditional call center metrics like AHT (Average Handle Time) or MTTR (Mean Time to Resolve) — they don't fit internal automation. Instead, focus on how well your chatbot actually helps employees and improves productivity.
Key engagement metrics to track:
Task completion rate. How often do employees successfully get what they need (e.g., “Show me the travel policy” or “Request a new laptop”) without human intervention?
Fallback or escalation rate. How often does the bot fail to answer and escalate to HR, IT, or another department? Frequent escalation suggests your knowledge base needs expansion.
Reuse rate. How often do employees return to the chatbot? A growing reuse rate signals trust, usefulness, and time savings.
✍️ Define clear KPIs from the start. Your AI chatbot KPIs should directly connect to business or operational goals. Each one should be:
- Straightforward and easy to measure
- Quantifiable, with before-and-after comparisons
- Linked to real financial value — for example, calculate how many work hours (and therefore costs) your bot saves each month.
Start small, then scale. Instead of chasing massive ROI from day one, aim for incremental wins — like automating one HR process or reducing routine IT requests by 10%. Once the chatbot proves its worth, gradually expand its scope to other functions.
Never measured chatbot ROI before? We've compiled a complete guide covering everything you need to consider to get an accurate view of your AI project's actual impact.
Step 11: Scale and Drive Culture Change
Once the pilot succeeds, it's time to expand. Introduce your chatbot to new departments or use cases — HR, IT support, procurement, or operations. Document your workflows and best practices to create an internal AI playbook that other teams can follow.
To sustain long-term success:
- Provide continuous training for employees as the chatbot evolves.
- Encourage teams to experiment and suggest new automation opportunities.
- Foster a culture that sees AI not as a replacement — but as a collaborative assistant that makes work easier and more efficient.
That's how an internal chatbot grows from a simple pilot into a powerful tool that transforms how your organization works.
Building a Secure, High-Impact Internal Chatbots
Following these steps helps organizations launch an internal AI chatbot that employees trust and actually use. With stakeholder alignment, careful promotion, human oversight, and a secure foundation, your chatbot can automate FAQs for employees, reduce workload for HR, IT, and support teams, and deliver measurable operational impact.
Invest in a chatbot your team can rely on. Book a demo to see how secure, accurate AI support can transform employee assistance.
Transform Employee Support. Discover the power of AI-driven internal chatbots.