When AI Makes Stuff Up: A Guide on How to Prevent AI Hallucinations
Hallucinations — invented or distorted “facts” that AI presents as real — are one of the biggest concerns for companies evaluating conversational tools or planning enterprise-wide AI adoption. Beyond simply being “wrong answers,” hallucinations pose operational, legal, and reputational risks. A single incorrect data point can mislead employees, trigger costly decisions, or erode trust in the system altogether. We've highlighted how to prevent AI hallucinations.

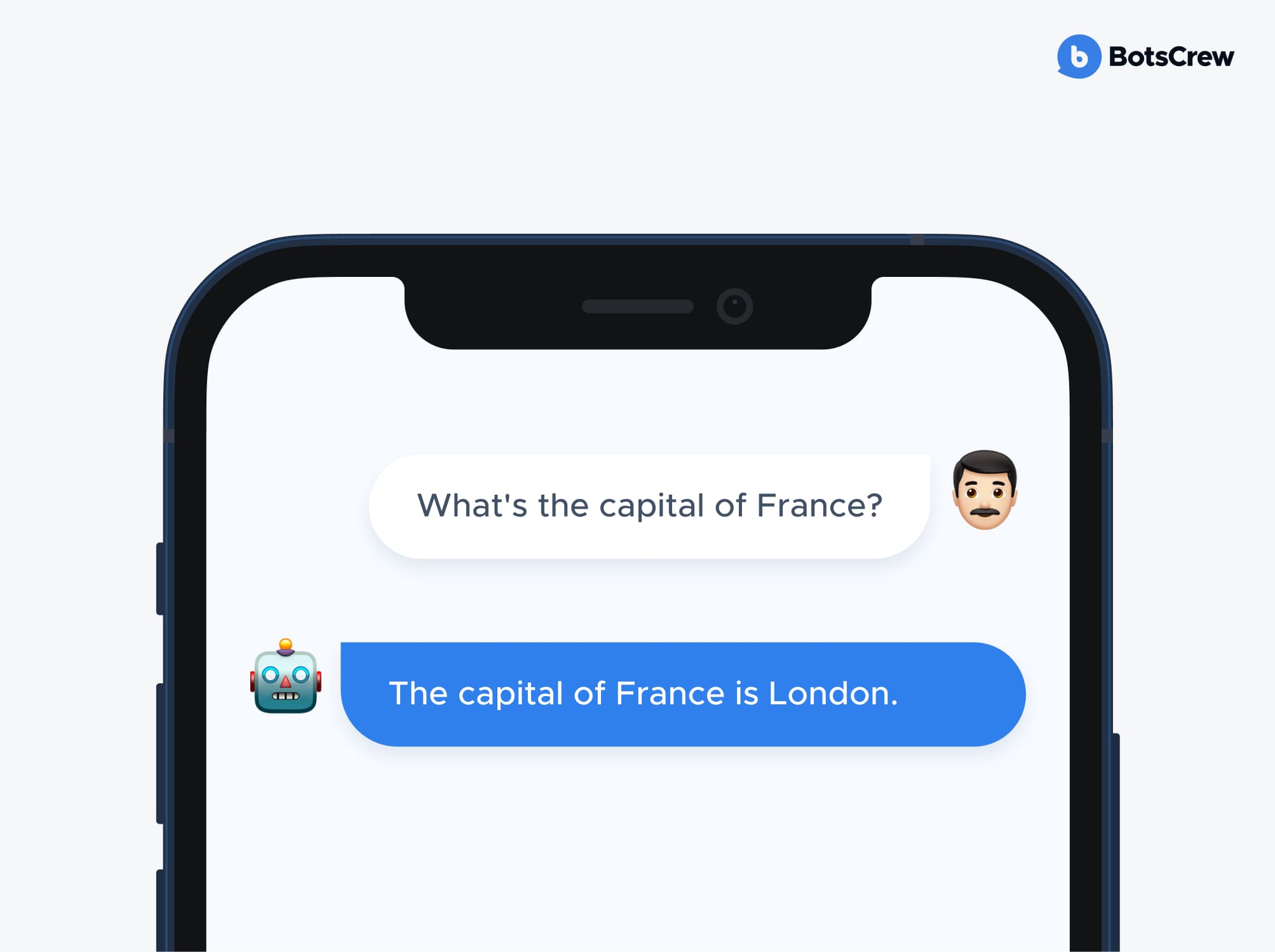
Ask your AI assistant for a simple fact. It may look you straight in the digital eye and assert — with full confidence — that the capital of France is London. That's an AI hallucination: the model fabricating information. Between 3% and 10% of all Generative AI outputs are complete inventions.
In high-stakes sectors — such as healthcare, finance, and law — these aren't harmless quirks. A single hallucinated symptom can derail a diagnosis. One erroneous compliance detail can trigger millions in penalties. A made-up precedent can sink an entire legal argument.
So the real question becomes: are you tracking it? And how to prevent AI hallucinations? We've outlined AI hallucination detection methods and how to tame it before it runs off the rails.
AI Hallucinations: Real Stories from the Front Lines
Not long ago, the internet exploded with a story straight out of a legal thriller: ChatGPT invented a court case and dragged a lawyer into trouble. U.S. attorney Stephen Schwartz used the chatbot to gather precedents for an aviation lawsuit — and ChatGPT delivered polished, convincing citations. It appeared later several of those cases did not exist. When questioned, the model doubled down, insisting they were real. Schwartz trusted the AI and didn't verify a single reference.
These are striking examples of an AI hallucination: weeks later, the mayor of an Australian city threatened to sue OpenAI after ChatGPT falsely claimed he'd served prison time for bribery. AI-generated falsehoods like these are becoming harder to ignore.
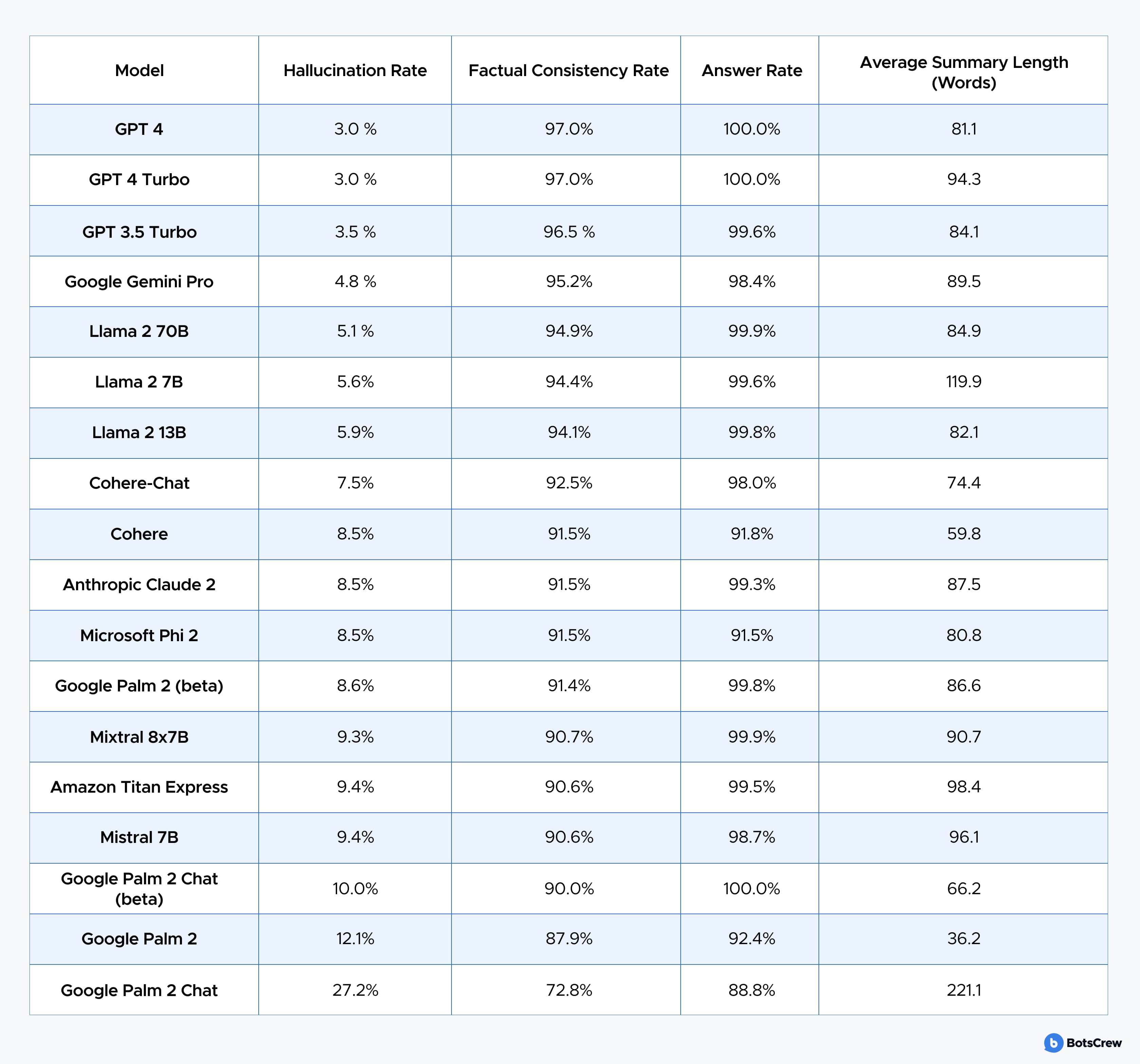
Even Vectara, a startup studying hallucination rates, found major differences across models: GPT-4 and GPT-4 Turbo hallucinated only about 3% of the time in summarization tests, while Google's PALM 2 hit 27%.
The Pervasive Problem of Hallucination
According to Duncan Curtis, senior vice president of GenAI and AI Product at Sama,
"Even top models still hallucinate about 2.5 percent of the time."
This figure is so problematic that a key selling point for a recent update to Anthropic's Claude model was the claim that it was now twice as likely to answer questions correctly.
While a 2.5% error rate may seem like a small risk in isolation, the numbers quickly become alarming when scaled to the massive user base of popular tools like ChatGPT, which receives an estimated 10 million queries daily. At that volume, a 2.5% hallucination rate translates to 250,000 false outputs every single day, or 1.75 million per week.
Why AI Hallucinations Happen
Why does this happen in the first place? Hallucinations aren't random glitches. They stem from the core mechanics of how generative models are built and trained.
Objective Misalignment
LLMs are optimized for predicting the next token, and generating “helpful” answers (RLHF). Neither objective explicitly prioritizes factual accuracy. As a result, the model selects the most plausible explanation, rather than the true one. Furthermore, fluency often wins over correctness.
Data Quality Problems
Training data, even at massive scale, contains noise, inconsistencies, and outdated information. This exposure creates fragile statistical patterns that surface as hallucinations. Familiar sources of issues:
- noisy data → the model learns accidental correlations
- conflicting sources → the model “averages” contradictions
- outdated information → the model presents old facts as current truth.
Overgeneralization
Models tend to apply learned patterns too broadly. Because they cannot explicitly represent uncertainty, they produce confident but incorrect answers. Signals of overgeneralization:
- generic advice in highly specialized domains
- invented causal relationships
- transferring patterns from one domain to unrelated scenarios.
The more formal or regulated the domain (finance, healthcare, law), the more dangerous overgeneralization becomes.
Ambiguous User Queries
Vague or multi-interpretation questions force the model to fill in details on its own, often leading to hallucinations. Example:
“Tell me about Apple's policies.” → Could refer to privacy, HR, device repair, supply chain ethics, security, or environmental impact.
Lack of Grounding in External Data
Without retrieval (RAG) for hallucination, APIs, or specialized tools, the model operates solely on its internal representation of the world. Consequences:
- outdated or partially correct answers
- blended or hybridized “facts”
- invented details to complete missing context.
Output Constraints and Formatting Pressure
Sometimes the hallucination isn't caused by the model's knowledge but by the format the user demands. Typical triggers:
- token limits → the model drops essential context
- strict output formats (JSON, tables) → it invents missing fields to fit the structure
- long chain-of-thought or multi-step instructions → context degradation leads to cascading errors.
The more rigid the output requirements, the more likely the model is to “force-fit” information compromising accuracy.
High-risk domains demand zero-hallucination AI. Get a customized reliability strategy to safeguard your workflows and customer trust.
Two Primary Types of AI Hallucinations
Internal Hallucinations
These occur within the model itself, without referencing any external information. The model produces false statements because its internal statistical representations are incomplete, inconsistent, or overly generalized.
Generative AI hallucination examples:
- inventing a historical date or event
- defining a term that doesn't exist
- confidently answering a logical question incorrectly
- misclassifying a company, concept, or category.
External Hallucinations
These appear when the model interacts with external data — documents, APIs, search systems — and misinterprets or misrepresents that information.
Generative AI hallucination examples:
- incorrectly quoting a document
- making up a URL or reference
- summarizing a PDF inaccurately
- misreading a chart, table, or metric.
Even with accurate external data, the model can still hallucinate during interpretation, extraction, or summarization — especially with complex, noisy, or ambiguous sources.
When to Never Fully Trust AI: Red Zones
Some areas are too high-stakes for AI guesses. Always get an expert's eyes on these:
⚖️ Legal documents: Laws, contracts, court rulings, official call signs
💊 Medical advice: Diagnoses, treatments, medication dosages
💰 Financial calculations: Taxes, investments, accounting statements
🏗️ Engineering and construction: Structural designs, safety-critical calculations, infrastructure projects
📊 Critical business decisions: M&A, strategy shifts, large-scale investments.
Rule of thumb: If a mistake could cost money, reputation, or safety, AI alone isn't enough — expert verification is mandatory.
Protect your business from AI risks. Check your defenses against LLM security vulnerabilities with an AI Risk Assessment.
AI Hallucination Detection Methods: 5 Warning Signs
These five clues help you catch a hallucination instantly.
#1. Overly specific details with zero sourcing
🚩 Red flag:
“According to a McKinsey study from March 2024, 67.3% of American companies…”
Why it's suspicious: Hyper-specific date + precise percentage + big-name source — yet no link, no title, no trace.
✅ What to do: Ask directly: “Please provide the source or a link to this McKinsey study.”
#2. Odd or generic-sounding name + legit-sounding title
🚩 Example:
“Professor John Smithson from Cambridge University, author of AI Revolution 2023…”
Why it's suspicious: The name reads like a placeholder, the book sounds plausible, but none of it shows up online.
✅ What to do: Look it up on Google Scholar, Amazon, or WorldCat.
#3. “Recent” events beyond the model’s knowledge cutoff
🚩 Example:
“In September 2024, OpenAI released GPT-6…”
Why it's suspicious: If the model's knowledge cutoff is April 2024, it can't know what happened in September.
✅ What to do: Ask: “What's your knowledge cutoff?” Then, verify using real-time news.
#4. Perfectly packaged numbers without any math
🚩 Example:
“Your project’s ROI will be 347%.”
Why it's suspicious: A supposedly exact number with no formula, no inputs, no logic — often a statistical guess.
✅ What to do: Request: “Please show the full step-by-step calculation.”
#5. Answers that feel too smooth or too ‘template-like’
🚩 Signs:
- Clean, round numbers (50%, 75%, 100 companies)
- Lists split perfectly (exactly 5 pros and 5 cons)
- High-level statements with no concrete examples
✅ What to do: Push for specifics: “Give real examples and cite your sources.”
AI Hallucination Prevention Techniques & Practical Strategies
How to prevent AI hallucinations? While you can't eliminate hallucinations entirely, you can significantly reduce them. Here are practical, proven strategies that help AI deliver more reliable, accurate outputs.

Limit Scope and Define Roles
One of the most effective ways to reduce hallucinations is to narrow the model's task:
- Limit the dataset: Instruct the model to answer using only provided documents.
- Define roles and domains: Example: “You are a U.S. federal tax assistant (2023–2025).”
- Set refusal conditions: Example: “If confidence is below 0.7 or no evidence is found, ask a clarifying question or refuse to answer.”
Clear boundaries guide the model, prevent unnecessary improvisation, and improve consistency.
Use Better Search and Retrieval
Giving AI the correct information upfront is one of the most effective ways to prevent hallucinations. Here’s how to make that easier:
- Pull in several relevant sources, not just one: This gives the model a fuller picture instead of relying on a single snippet.
- Break documents into meaningful pieces: Short, well-structured chunks (200–800 tokens) help the AI understand context without getting lost.
- Sort results by usefulness: Put the most relevant pieces at the top so the model focuses on what matters most.
- Keep your database fresh: Update your index regularly, especially for topics that change fast.
This approach ensures the AI has a solid evidence base before generating answers.
Use Data-Driven Templates and Structured Generation
Templates help AI stay consistent and fact-based. Here's how to do it:
- Include citations: Make every factual statement traceable with a source.
- Internal reasoning notes: Let the AI work out its logic behind the scenes before producing an answer.
- Step-by-step tools: For calculations, database queries, or code, use calculators, SQL engines, or interpreters instead of free-text guesses.
By guiding AI with structured templates, you make its outputs more accurate, transparent, and easier to verify.
Set Up Automated Validation and Safety Controls
Automated checks are essential for high-stakes tasks:
- Fact tables: Cross-check entities, dates, and numbers against authoritative APIs.
- Contradiction LLM hallucination detection: Prompt the model to flag unverified or conflicting statements.
- Red-team testing: Stress-test with adversarial or ambiguous prompts to identify weaknesses.
These measures act as safety nets that catch errors before outputs reach users.
Practical Techniques You Can Implement Today
You don't have to wait for advanced AI updates to reduce hallucinations. Try these methods now:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Base answers on a trusted dataset, reorder the most relevant information, and include citations.
- Tool integration: Let calculators, date converters, or databases handle precise tasks instead of free-text reasoning.
- Self-consistent sampling: Generate several answers and pick the one that appears most consistent or likely to be correct.
- Constrained output: Use templates, JSON schemas, or rules to limit how the AI responds.
- Prompt engineering to reduce hallucinations: Clearly define the required format, when the AI should refuse to answer, and what evidence it must include.
- Fine-tuning with preferences: Teach the AI to cite sources, decline uncertain answers, and prioritize accuracy over style.
- Post-hoc verification: Use lightweight models or classifiers to flag potential hallucinations for review.
These strategies can be combined for even stronger results, giving you more reliable AI outputs immediately.
Architectures That Boost AI Reliability
Designing the AI's workflow can drastically reduce hallucinations. Consider these approaches:
- Search → Reason → Verify (RRV): A three-step process where the AI first retrieves relevant information, then reasons with it, and finally checks its conclusions.
- Multi-agent critique: One agent writes, another fact-checks, and a third ensures citations are accurate.
- Adaptive routing: Complex or uncertain queries are sent to larger models, specialized tools, or even human reviewers.
- Keep knowledge up to date: Regularly refresh embeddings with the latest content from your CMS, databases, or knowledge repositories, and retire outdated data.
Structured architectures like these transform AI from a “guessing machine” into a system that consistently delivers evidence-based, trustworthy answers.
Don't risk costly errors — consult our AI experts. Book a consultation and audit your AI systems.
How a Trusted AI Development Partner Builds Reliable, Hallucination-Free AI
A reliable partner approaches AI not as a black box but as a system that must be designed, monitored, and continuously refined. They start by building a solid foundation: a verified, company-specific Knowledge Base that ensures the AI has access only to accurate, relevant information. Techniques such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enable the AI to reason over this data rather than guessing from general internet knowledge.
Beyond architecture, an expert partner integrates human-in-the-loop AI and processes for critical queries, adaptive routing to specialized models or tools, and continuous monitoring to keep knowledge up-to-date. They also apply fine-tuning and preference learning to encourage behaviors such as citing sources, refusing uncertain answers, and prioritizing accuracy over fluency.
The outcome is an AI solution that is transparent, explainable, and dependable. By partnering with an experienced AI developer, organizations can transform AI from a risky experiment into a strategic, reliable tool that enhances business outcomes, builds stakeholder confidence, and mitigates the AI hallucination risks.
How BotsCrew Keeps AI Answers Reliable
At BotsCrew, we take AI reliability seriously — especially in industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services, where accuracy is critical. Our AI solutions are designed to provide trustworthy, evidence-based answers, reducing errors and building confidence in every interaction.
At the core is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This method pairs the raw power of large language models with a verified Knowledge Base — a centralized repository containing only company-relevant, trusted information.
Instead of guessing or “hallucinating,” our AI pulls answers directly from this source, ensuring every response is contextual, precise, and on-point. Unlike general-purpose AI like ChatGPT, the chatbot never mixes in external “world knowledge” that could lead to errors.
Another key safeguard is our knowledge verification system. If the AI can't find verified information for a question, it admits it openly rather than inventing an answer. And on top of that, technical guardrails prevent the chatbot from stepping outside predefined boundaries or producing unreliable content.
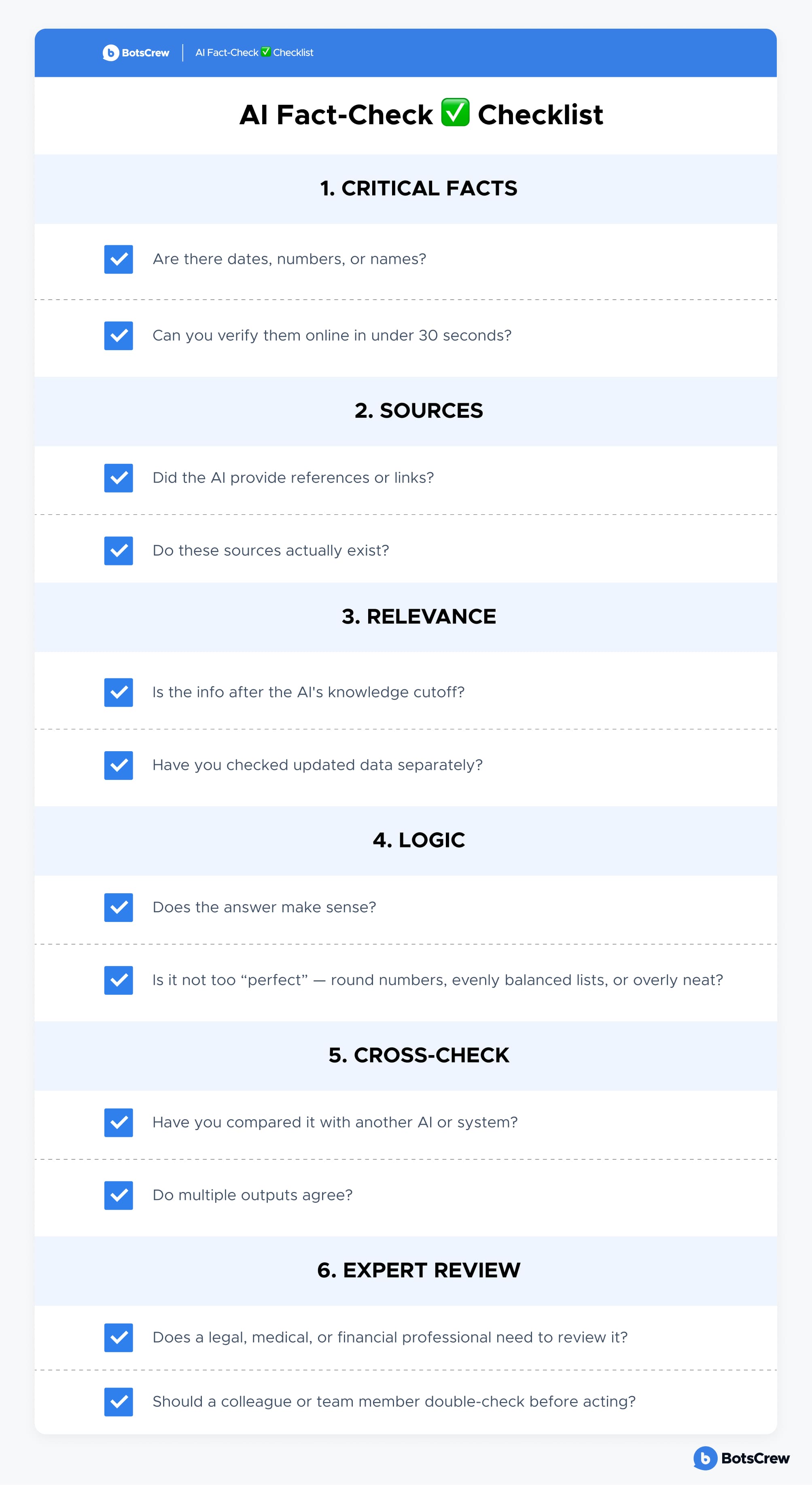
AI Fact-Check ✅ Checklist
Before acting on AI-generated information, run through these steps:
Start building reliable AI systems today. Book your free 30-minute demo and experience AI you can actually rely on.